Kieran’s Our City, Our Town Article,
Cork Independent, 10 March 2016
Cork Harbour Memories (Part 52)
A Besieged Cork 1642
The defence of County Cork from the Confederate army rested with the Lord President of Munster, Sir William St Leger (1586 –1642). Very little is compiled in a general sense of what happened in the wars around the walled town of Cork. I came across an interesting and old article on the Siege of Cork in 1642 by James Buckley in the “Journal of the Cork Historical and Archaeological Society” from 1916. In an attempt to reconstruct a balanced point of view, he draws from seventeenth century manuscripts, letters and House of Commons speeches. He denotes that in the year leading up to Liscarroll and West Cork battles in 1642 (see previous articles), St Leger frequently requested for men of war and munitions from Dublin.
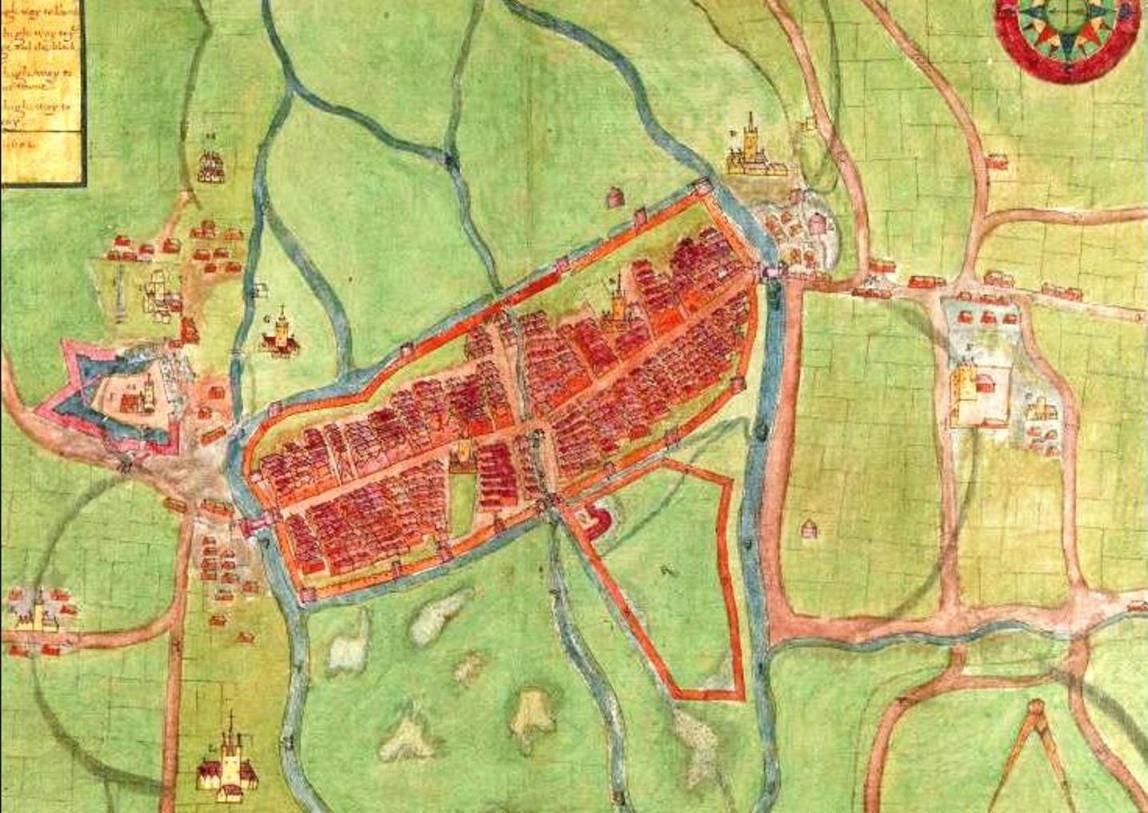
In February 1642 St Leger resolved on abandoning the open country of County Cork in an effort to keep a few ports open and to keep open his sea communication with Dublin. St Leger evacuated his home at Doneraile and withdrew to the walled town of Cork. The exact troop of force that retreated with him is not definitely known but there is an estimate of 2,000 foot soldiers and two complete troops of horse. A considerable number of English settlers in County Tipperary and other parts of Munster also withdrew to Cork and Youghal for protection. In addition to the retreating forces the walled town of Cork probably possessed a number of sympathisers capable of bearing arms. The batteries at Elizabeth Fort and Shandon Castle (now the site of Firkin Crane) were manned, and it is estimated that St Leger then had close on 3,000 effective foot soldiers at his command.
On St Leger securing himself within the gates of the walled town of Cork, the Irish Army approached the settlement and they blocaded the town preventing the landing of fresh troops. The army divided into two sections, one of which was under the command of Jeremy Long, the High Sheriff of the County, and Barry Óg. They were quartered at Belgooly, three miles to the north of Kinsale; the other commanded by General Barry, was encamped at Rochfordstown, three miles to the south of the town. These forces had participated in other battles as well in County Cork – comprising an estimate of some 3,000 foot soldiers. They were afterwards reinforced from West Cork and Kerry, but their combined number is quite uncertain, and probably fluctuated from 4,000 to 6,000 foot soldiers with perhaps a hundred horse.
One event that affected both sides was the landing of English commander Sir Charles Vavasour at Youghal on 20 February 1642, with 1,000 foot soldiers. He relieved the town that was then closely besieged by the Confederates. He then pushed his army into County Waterford. He provided hope of breaking Irish lines and kept the sea link open between Youghal and Cork. Meanwhile reinforcements still kept pouring into the walled town of Cork. On 18 March, Lord Inchiquin, a son-in-law of St Leger, landed at Youghal from Minehead, and on 20 March put to sea for Cork. Captain Pigott arrived from Dublin about the same time with fifty of St Leger’s old company. Captain William Jephson, with two troops of horse, 100 in each troop, one for himself and the other for Lord Inchiquin, landed at Youghal on the 19 March, and brought over a quantity of powder and ammunition, and reached Mallow with both troops about 25 March.
The walled town was besieged on the north side by Lord Muskerry, MacCarthy Reagh, and many of the chieftains of the western districts. St Leger heard that Lord Roche, Lord Ikerrin, Lord Dunboyne, the Baron of Loghmoe, Richard Butler, brother to the Earl of Ormond, and all the Tipperary forces were drawing together with the object of beleaguering him on the south side. In the first week of April 1642, he ordered the two troops of horse recently landed to create a diversion in north-east Cork under the command of Lord Inchiquin and Captain Jephson. This movement resulted in guerrilla warfare with some minor success. They relieved Rathgogan Castle (in present day Charleville), Ballyhay Castle and re-established a garrison at Doneraile. The two captains then withdrew to the city.
On 5 April 1642 the Irish forces at Belgooly struck camp and joined the main body near Cork. Owing to an absence of cannon, muskets and ammunition, the Irish confederates were unable to storm the walled town. This position continued till 13 April when an incident occurred. On the morning of that day a party from the Cork garrison was out on a scouting and foraging expedition. They encountered a detachment of the Irish a mile or so from the city, who drove them back to the suburbs. The English captains came forth with four troops of horse and 600 musketeers. They drove back the Irish and attacked a party then in ambush. Support from the Irish lines came forward, but all were pushed back in disorder. The English then rushed forward and took the main body by surprise. The cavalry broke in and disordered the lines and a general retreat was called. The Irish then scattered, many advancing into County Limerick to help with the Confederate war there.
To be continued…
Captions:
834a. A description of the Cittie of Cork/ Plan of Cork, circa 1602 by George Carew, showing Elizabeth Fort on the left and Shandon Castle on the right (source: Hardiman Atlas, Library of Trinity College Dublin)
834b. Section of Down survey map of Cork City, c.1655/56 (source: Cork City Library)