Kieran’s Our City, Our Town Article,
Cork Independent, 8 October 2015
Cork Harbour Memories (Part 32)
The Theatre of Empire
The online map archive of the city through the ages makes for great viewing at www.corkpastandpresent.ie. The early seventeenth century is well represented. One beautifully engraved and hand-coloured map is by John Speed (1552-1629) of the province of Munster taken from The Theatre of the Empire of Great Britaine (1611-12). In the corner of the map is a representation of the walled town of Cork. Though dated 1610 and mentioning London based publishers John Sudbury and George Humble. It was 1616 before it was actually published in Amsterdam by globe maker and map engraver Jodocus II Hondius with the assistance of George Humble, who also acted as Speed’s editor. Sudbury and Humble were the largest and most successful publishers and print-sellers in London.
The Munster map is embellished with an engraving of a man (a cartographer?) wielding a large pair of dividers, while he stands on top of the scale of Irish miles; in Youghal harbour is a galleon ship and in the Atlantic is a boy playing the harp whilst sitting astride a remarkable winged sea creature. Present day Munster comprises six Irish counties but the province has to this day many churches and ancient castles that are depicted on this map. The map abounds with the names of local clans and families – it is inscribed in a very personal way – but its use was also political showing the controlled hidden corners of the British empire.
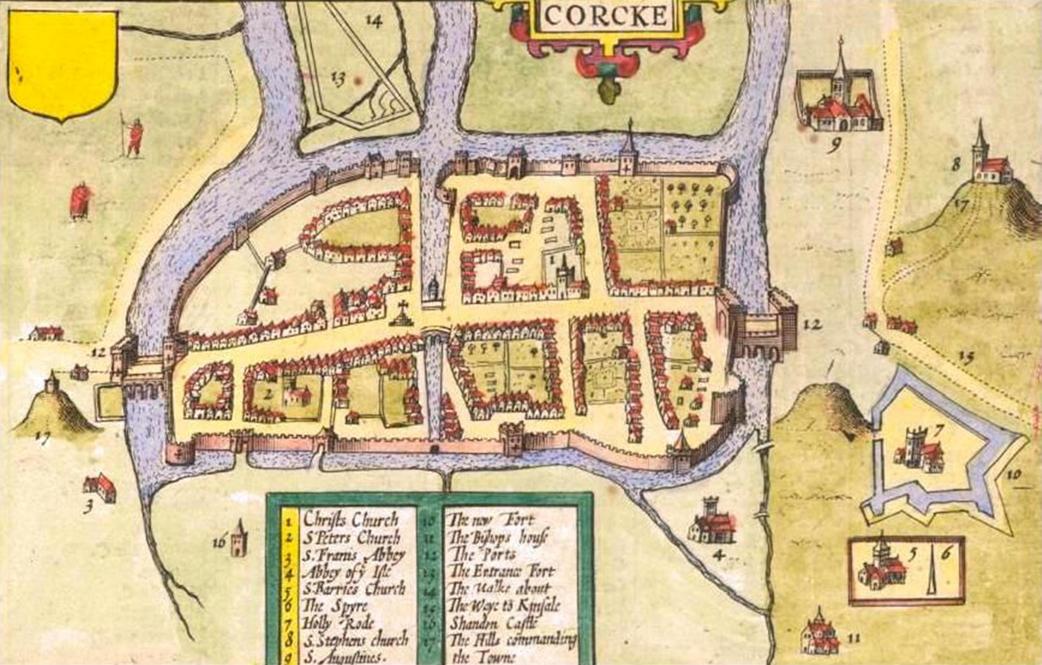
There are two inset town plans on the map of the most prominent towns in the province at the time – Cork and Limerick, both of which were fortified with large town walls and built on rivers. In the Cork map, the northern suburbs, present day Shandon Street is shown along with Shandon Castle and the remains of the Franciscan Abbey on the present day site of the North Mall. In the southern suburbs, structures such as the Augustinian Abbey, the earthen ramparts of Elizabeth Fort, while further west an old medieval church associated with the remains of a round tower encompassed by a wall are depicted.
The Oxford Dictionary of National Biography records that John Speed as beginning his working life as a tailor in the northern English county of Cheshire. He pursued his apprenticeship under his father, a local tailor, and carried on the family business for a number of years. His attention to detail and a keen interest in cartography, led him to try his hand at map making. He began to display a uncharacteristic talent for this and, despite still working as a tailor, Speed created and published his first known map in 1595 – a map of Canaan.
Soon afterwards, Speed was patronised by Sir Fulk Revil, It was this generosity that allowed Speed to depart for London, still as a teenager, and focus on his education at the College of Antiquaries. He became absorbed in his studies, developing his keen interest in history, and soon a specialist interest in the history of cartography. With the help and advice of various associates of Sir Fulk Revil, he pursued the notion of creating a complete and precise atlas of the British Isles.
Speed took the first step with his home county of Cheshire, completing the map with one of the earliest town plans of Chester with arms and vignettes which were to become his signature style. Engraved by William Rogers, this map was published individually in 1604. He continued to cover all the counties of England and Wales. The resulting atlas, finally published in 1612, was titled The Theatre of the Empire of Great Britaine. This remarkable work was published in partnership with the already established house of John Sudbury and George Humble. The atlas, bought by the University Library in 1968, is now considered priceless. It contains a single sheet for each county of England and Wales, plus a map of Scotland and each of the four Irish provinces, and paints a rich picture of the countryside at the turn of the seventeenth century. Cambridge University Library is home to one of only five surviving proof sets. Their map department elegantly describes Speed’s maps: “Rivers wriggle through the landscape, towns are shown as huddles of miniature buildings, woods and parks marked by tiny trees and – with contour lines yet to be invented – small scatterings of molehills denote higher ground”.
The ‘Theatre’ was a great success and was published again many times and by a number of publishers: Sudbury and Humble notably published their second edition of The Theatre in 1627, the last edition to be published before Speed died. In 1627, Speed released his other major work: A Prospect of the Most Famous Parts of the World. This finely detailed and embellished world atlas, the result of many years development alongside The Theatre, includes the notable accolade of being the first world atlas to be published by an Englishman. The Prospect was to be his last major work. John Speed died on 28 July 1629 having created some of the most remarkable cartography.
To be continued…
Captions:
813a. Section of John Speed’s Province of Munster, from Speed’s The Theatre of the Empire of Great Britaine, c.1610-11 (source: Cork City Library)
813b. John Speed’s ‘Corke’ from his Province of Munster (source: Cork City Library)